Rapid Reference
Workup
- Labor: HypoK+? HypoMg2+? Hyperthyreose? ggf. Digitalis-Spiegel?
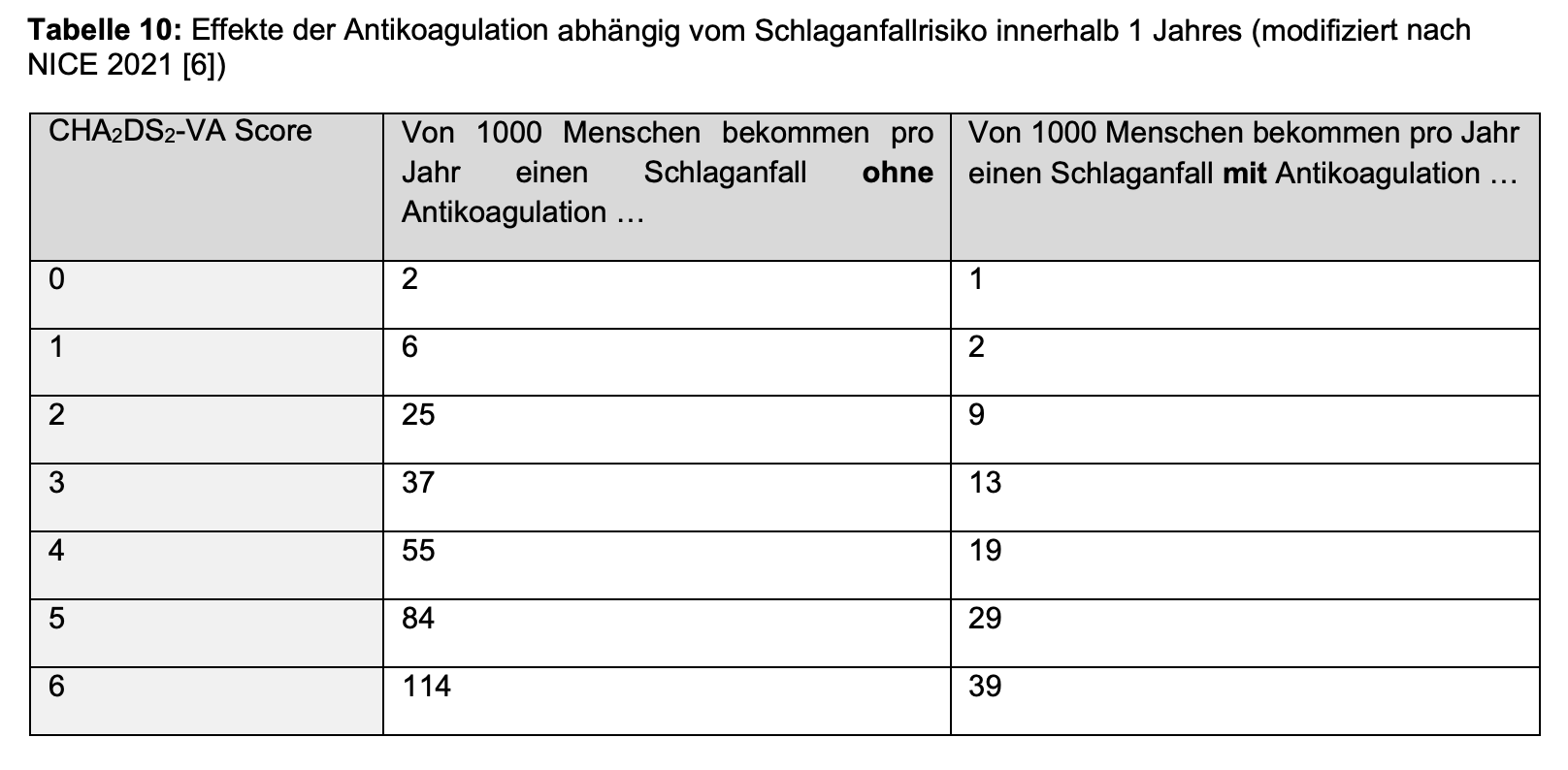
Antikoagulation bei VHF
- Indikation AK bei CHA2DS2VA-Score ≥2 Pkt.
- Chronische Herzinsuffizienz
- Hypertonie
- Alter >75 J. (2 Pkt.)
- Diabetes
- Stroke / TIA / Thromboembolie (2 Pkt.)
- Vaskuläre Vorerkrankung: KHK, pAVK
- Alter 65-75 J.
- Indikation AK: HCM oder kardiale Amyloidose
- Indikation VKA: Valvuläres VHF (Mitralklappenstenose ≥2° oder MK-Ersatz)
- Nach eKV: CHA2DS2VA ≥1 oder VHF >24h: AK 4 Wochen, dann Reevaluation
- HAS-BLED nicht mehr empfohlen
Antikoagulation
Textbaustein Diagnose VHF
Aktuell: Intermittierendes/Persistierendes/Permanentes, bradykardes/normofrequentes/tachykardes Vorhofflimmern (VHF), ED ### - ##.##.####: CHA2DS2-VASc: ### - ##.##.####: eKV - ##.##.####: Ablation - OAK mit
Literatur
- S3-Leitlinie Vorhofflimmern
- Koffein verursacht wahrscheinlich zumindest kein VHF, in 1 RCT sogar geringere Recurrence2
Footnotes
-
HF 120-180 normalerweise maximal ohne AV-Block / neg. Dromotropie, bei >200/FBI DD VHF + WPW ↩
-
Wong CX. Caffeinated Coffee Consumption or Abstinence to Reduce Atrial Fibrillation: The DECAF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Nov 9:e2521056. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.21056. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 41206802; PMCID: PMC12598581. ↩